OMEGA-3 FATTY ACIDS
Treasures
for your health
What are Omega-3 fatty acids?
Necessary fatty acids
Omega-3 are polyunsaturated fatty acids, which cannot be composed by the human body, and therefore it is necessary that they are acquired through nutrition.
The three main omega-3 fatty acids are:
- eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
- alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)
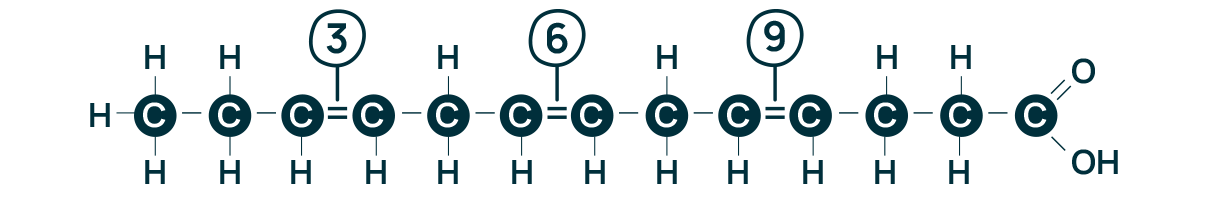
Omega-3/Omega-6/Omega-9
fatty acids
When counting carbons (C), one starts from the last one, therefore fatty acids are called “omega” named after the last letter of the Greek alphabet. The position where the first double bond between the (C)s lies finally defines the name of each fatty acid.
Sufficient intake
Multiple benefits
The ALA acquired through nutrition is transformed to EPA and DHA to be used by the human body. The quantity transformed is very small and not sufficient to cover the daily needs of the human body. Direct intake of EPA and DHA from food and/or food supplements offers the maximum advantages of the omega-3 fatty acids.
They affect cardiovascular and cerebral functions, they benefit health of the skin and bones, they help in preventing cancer etc. They can be found in high concentration in the retina of the eyes and they are part of the structure of the cell membranes.
DHA and EPA
The differences between them
DHA contributes into the healthy function of the human heart, eyes, and brain. High quantities of DHA are already necessary since pregnancy, as they affect both the healthy growth of the foetus and the upcoming good health of the baby up to the age of three.
EPA has been found to aid the immune response of the human body, to contribute to the health of bones and muscles, while it also has anti-inflammatory traits.
Although they do not contribute to health in the same way, they act complementing each other and are necessary in sufficient quantities to offer their benefits
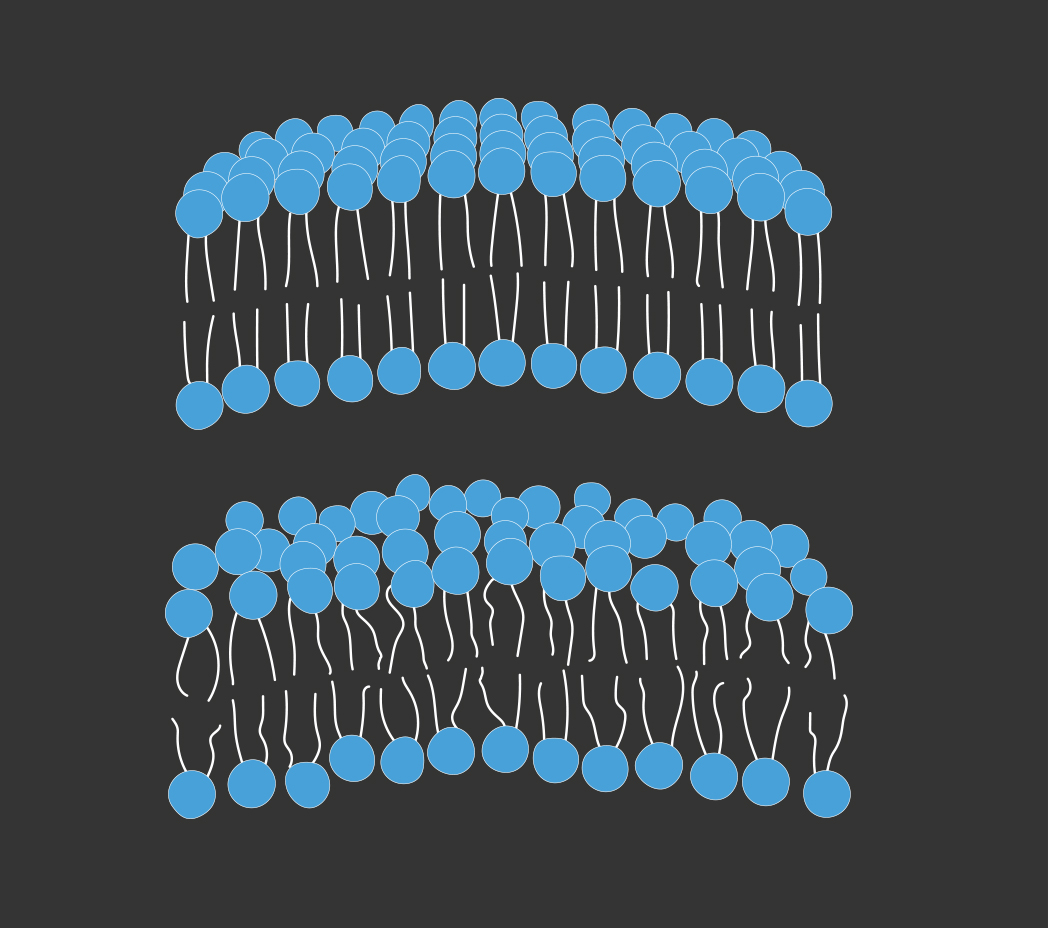
The omega-3 and structure of cellular membrane
The double bonds in the chain of unsaturated fatty acids create bends and folds.
The presence of unsaturated fatty acids in cellular membranes increase their fluidity and their capability to change form, allowing proteins and lipids to move, as well as to adapt and be resilient in cases of cellular membrane damage.
Cardiovascular function
The omega-3 have the capacity to protect the human heart from inflammations, which can cause damage to blood vessels that leads to cardiovascular events. They act by diminishing:
- triglycerides and LDL-cholesterol
- blood pressure
- coagulation of blood
- risk of cerebrovascular accidents (CVAs)
- irregular heart rate
The three most important Cardiological Associations worldwide have stated that, for people that have been through or at the risk of a heart attack, the intake of omega-3 fatty acids is necessary

People with an omega-3>8% index
have an average of
85,5 times
less risk
of a cardiovascular event
Suggested intake of omega-3 when one suffers from cardiovascular diseases
700-1.500mg/day |
Arteriosclerosis |
1.500mg/day |
Coronary heart disease |
1.500-4.000mg/day |
Triglycerides |
4.000mg/day |
High blood pressure |
Omega-3 and eye health
Omega-3 fatty acids, and more specifically DHA, are found in high levels in the eye retina. High quantities of omega-3 fatty acids contribute to the improvement of health and the proper function of the eyes, as well as to the relief of xerophthalmia symptoms, such as stinging, burning, and chafing.
People that consume sufficient quantities of omega-3 fatty acids face less risk of problems of eyesight

Omega-3 and brain function
Omega-3 fatty acids are necessary structural ingredients of the human brain and of neurons, and they are needed since foetal phase for the proper development of the brain through all stages of life. Their high intake contributes into strengthening memory and learning abilities, as well as into slowing down the aging of the brain.
Omega-3 and bone and muscle health
EPA and DHA moderate inflammatory reaction and they prevent bones from disintegrating. At the same time, they activate special kinds of cells that contribute to the creation of new bones. Through this entire process, the sufficiency of omega-3 fatty acids is necessary so that omega-6 fatty acids do not prevail, as when the balance of their proportions is not maintained, decrease of bone density and mass is possible.
Less inflammations and swellings in joints lead to less pain and less vulnerability

Omega-3 and pregnancy
Important for the mother and the proper growth of the foetus
The foetus needs DHA fatty acids, which it can acquire only through the mother. These fatty acids contribute into the proper growth of the brain and retina during pregnancy as well as during the early babyhood.

Doses of at least
500mg/day
have been found
to diminish the risk of
a premature birth
and an underweight baby
Healthy skin
Omega-3 fatty acids regulate the oiliness and contribute into the hydration of the skin. They are a strong ally against wrinkles and signs of aging, and they have the ability to relieve irritations and dermatitis symptoms for a shiny and soft skin.
Studies have found a correlation between EPA and DHA consumption and protection of the skin from unwanted effects of ultraviolet radiation.
Healthy, dense, and shiny hair
It has been proved that omega-3 fatty acids contribute to better blood circulation and better blood supply to the head’s hairy part and hair follicles. They protect hairs from breaking, they improve their density, and they help their right rate of growth, resulting into less loss of hairs and protection from it. At the same time, it has been shown that they slow down the hairs from aging, postponing the appearance of grey ones.

The alpha in omega
- High content 85% of omega-3 fatty acids
- No after fishy taste
- Small fish fished in Antarctica
- Molecular and Short Path distillation
- Anti-reflux formula
Fish from Antarctica
- The cleanest waters possible, without harming the environment
- Fish oil from small fish, sardines and anchovies, in which no toxic heavy metals are accumulated

Double method of distillation
Molecular distillation
It takes place 3 times, removing contaminants (heavy metals, dioxins, etc.), saturated fats and other unwanted organic compounds, keeping only the basic beneficiary ingredients of fish oil.
Short-path distillation
It is characterized by a “short-path” processing which is repeated twice. This processing effectively removes organic waste which cannot be taken away with molecular distillation. The temperature of heating is significantly lower, and the distillate needs to move across only a small distance before being concentrated. Therefore, there are no negative effects such as breaking or oxidation of the fish oil.

Total Oxidation Price
Totox Price
Low Totox price, high quality of fish oil
The Totox price is used to describe the total oxidation of the oil, which is one of the greatest threats for the fish oil. The oxidation of the oil percentage, in other words its low Totox price, indicates the purity of the product.
- Prices above 26 can cause toxicity to the human body
- Prices between 4 and 6 indicate a high purity and high-quality fish oil
The Totox price
for omegazym® is only 5,
indicating a fish oil of
high purity and quality
Deodorising method
Naturally, using water steam
The materials which cause unpleasant taste and odour are removed. The fish oil that results has a clear colour, without sediments, and improved properties. The process of deodorising omegazym® does not contain risks for human health, as damaging substances are not created through the process.
Omegazym® has been processed in a totally natural way, with the use of water steams. No chemical means have been used, and no fragrances have been added

Consumption without limits
Deodorising omegazym® facilitates easy consumption, leading into a pleasant experience in the intake of omega-3 fatty acids.
omegazym® capsules:
- Do not leave a taste of fish
- Anti – reflux formula

Anti-reflux formula
The omegazym® fish oil is processed in a special way, so that volatile substances that cause unpleasant side-effects through digestion are removed. In this way, no flatus are created in the stomach rising to the oesophagus and the mouth, and causing a sense of burning, odour and unpleasant taste.

Newsletter by Oloneans
Be the first to learn about new products and actions by OLONEA, and get informed on matters of health and scientific progress